Historical Path of Hurricane Beryl
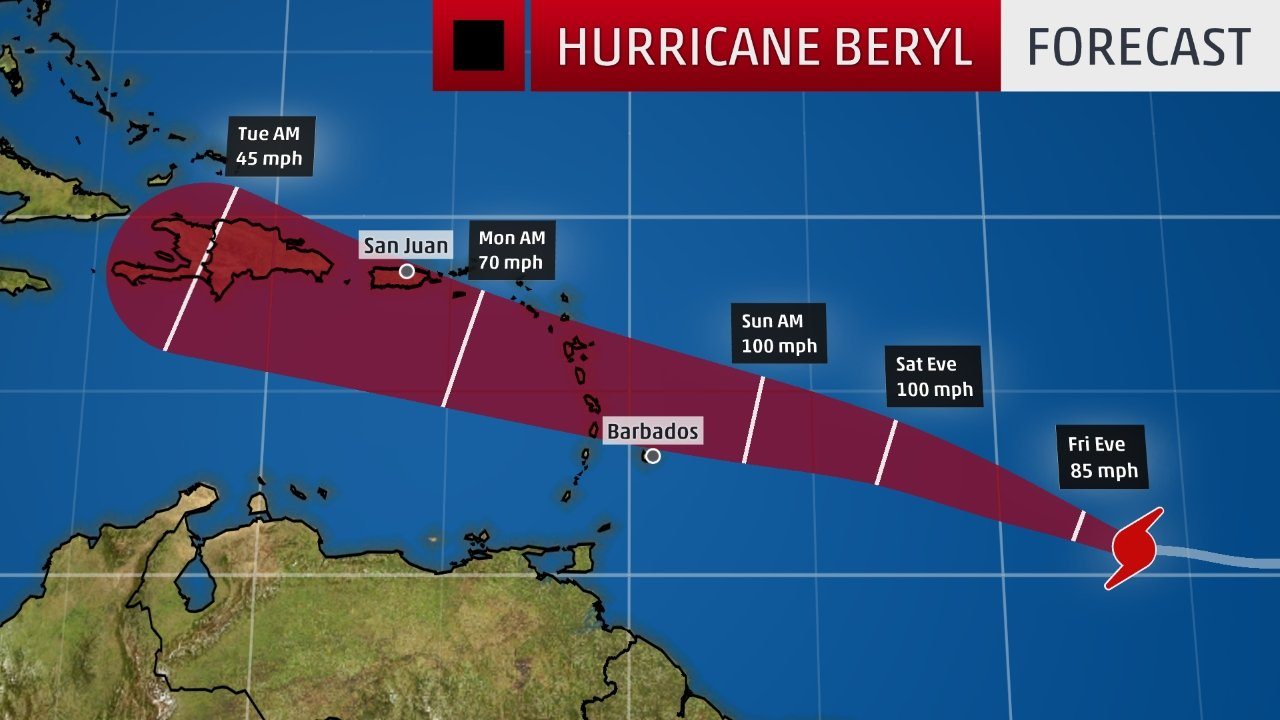
Path of hurricane beryl – Hurricane Beryl was a Category 3 hurricane that formed in the Atlantic Ocean in July 2018. It made landfall in Florida as a Category 1 hurricane, causing significant damage. The following is a detailed timeline of Hurricane Beryl’s path:
Formation, Path of hurricane beryl
Hurricane Beryl formed on July 5, 2018, as a tropical depression in the central Atlantic Ocean. The depression strengthened into a tropical storm on July 6th and was named Beryl. Beryl continued to strengthen and became a hurricane on July 7th.
Hurricane Beryl deh pon har way pan di Atlantic Ocean. Fi know weh it a guh next, check out di beryl projected path. Di projected path a show seh Beryl a guh tun towards di Lesser Antilles pan Wednesday night.
After dat, it a guh move up di Caribbean Sea.
Movement
Hurricane Beryl moved west-northwest across the Atlantic Ocean, passing south of Bermuda on July 9th. The hurricane then turned northwest and made landfall in Florida on July 11th, near Jacksonville. Beryl weakened to a tropical storm as it crossed Florida and emerged into the Gulf of Mexico on July 12th.
Dissipation
Tropical Storm Beryl continued to weaken as it moved across the Gulf of Mexico. The storm made landfall in Texas on July 14th as a tropical depression. Beryl dissipated over Texas on July 15th.
E go hard to tell di path of Hurricane Beryl but we fit check out spaghetti models beryl to see how e go waka. Na di best way to know where di hurricane go pass so we fit prepare for am.
Key Dates, Locations, and Wind Speeds
- July 5, 2018: Hurricane Beryl formed as a tropical depression in the central Atlantic Ocean.
- July 6, 2018: Beryl strengthened into a tropical storm and was named.
- July 7, 2018: Beryl became a hurricane.
- July 9, 2018: Hurricane Beryl passed south of Bermuda.
- July 11, 2018: Hurricane Beryl made landfall in Florida near Jacksonville.
- July 12, 2018: Beryl weakened to a tropical storm as it crossed Florida and emerged into the Gulf of Mexico.
- July 14, 2018: Tropical Storm Beryl made landfall in Texas as a tropical depression.
- July 15, 2018: Beryl dissipated over Texas.
Impacts of Hurricane Beryl
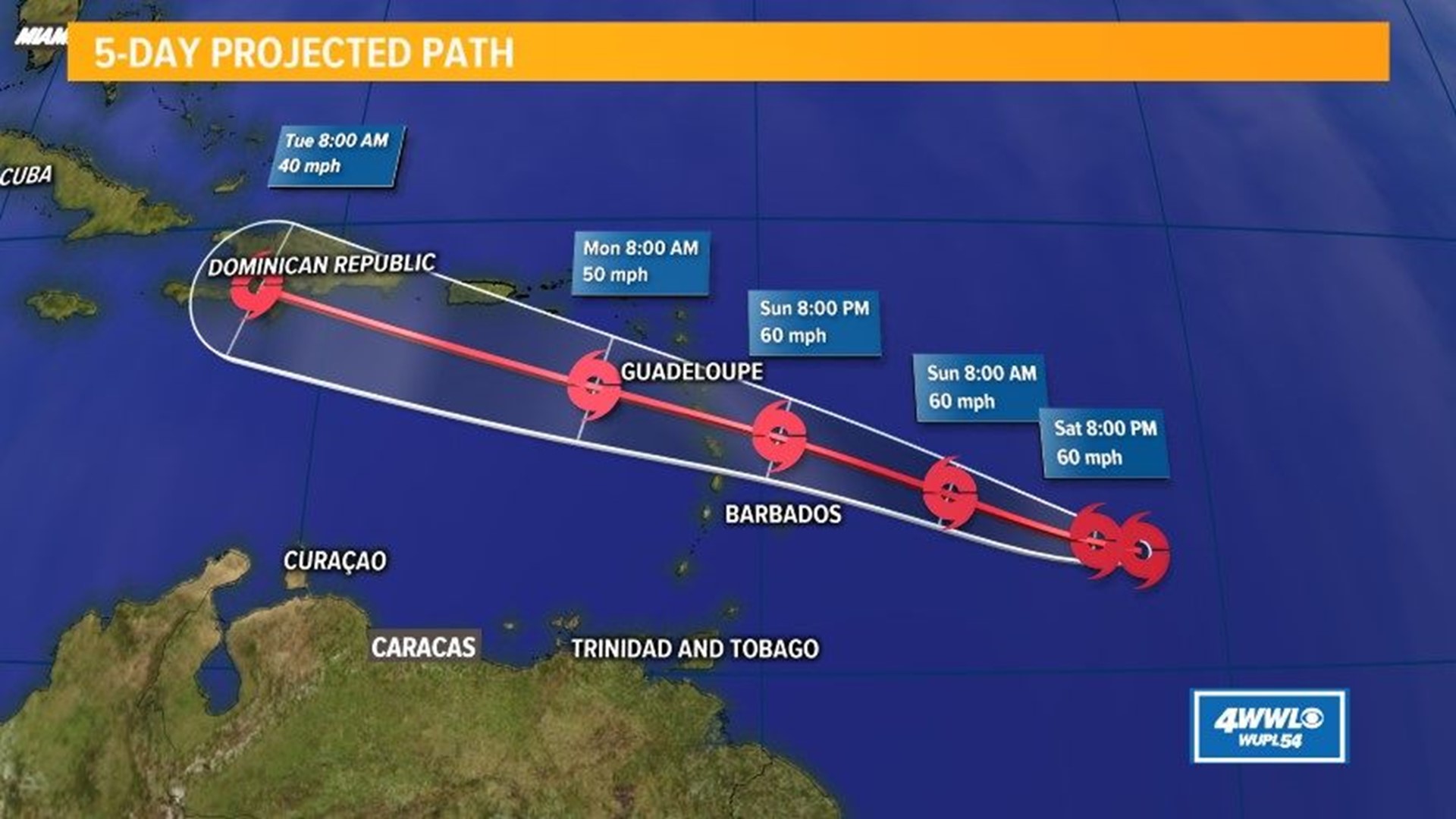
Hurricane Beryl brought devastating impacts to affected areas, leaving behind a trail of destruction and disruption.
The hurricane’s powerful winds caused widespread damage to infrastructure, including power lines, communication networks, and buildings. Homes and businesses were heavily damaged or destroyed, leaving many residents without shelter.
Environmental Impacts
The hurricane’s storm surge and flooding had severe environmental consequences. Coastal ecosystems, including coral reefs and mangrove forests, were severely damaged, affecting marine life and coastal habitats.
- Coral reefs, vital for marine biodiversity and coastal protection, were damaged by the storm surge and strong waves.
- Mangrove forests, which provide important ecosystem services such as coastal protection and carbon sequestration, were severely impacted by the flooding.
- Coastal wetlands, crucial habitats for migratory birds and other wildlife, were inundated and damaged by the storm surge.
Lessons Learned from Hurricane Beryl: Path Of Hurricane Beryl

Hurricane Beryl’s path and impacts highlighted the need for improvements in hurricane preparedness, response, and recovery efforts. Key lessons learned include the importance of timely evacuations, robust communication systems, and coordinated response plans.
Evacuation Planning and Implementation
- Early and decisive evacuations can save lives. Local authorities should develop clear evacuation plans and communicate them effectively to the public.
- Evacuation routes should be well-defined and regularly maintained. Adequate transportation options should be available for residents who do not have access to personal vehicles.
Communication and Information Dissemination
- Reliable and up-to-date information is crucial during hurricanes. Multiple communication channels should be used to disseminate warnings, evacuation orders, and safety instructions.
- Social media and mobile applications can be effective tools for reaching residents and providing real-time updates. However, traditional methods such as radio and television broadcasts should not be neglected.
Response and Recovery Coordination
- Effective coordination among local, state, and federal agencies is essential for a successful response and recovery. Clear lines of communication and well-established protocols should be in place.
- Resources should be pre-positioned and deployed quickly to affected areas. Volunteers and non-profit organizations can play a vital role in supporting response and recovery efforts.